While discussion of the concept of cultural and creative industries can be traced back to the 1940s, it was in the 1990s and 2000s when it started to gain relevance in the academic and political spheres
It is worth pointing out that UNESCO began using the expression Cultural Industries in the 70s, acknowledging the role they have as a framework for creation, expression and access to culture. UNESCO used the term in plural with the aim of reinforcing the singularities of the different cultural sectors.

Continuing with UNESCO, one of the most widely used definitions of the Cultural Industries is that approved in 2005, which identifies them with those activities which
“produce and distribute goods or services which, at the moment in which they are being created, are considered to have an specific attribute, use or purpose which embodies or transmits cultural expressions, irrespective of the commercial value they may have”
It was the United Nations (UN) who, at the Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), had expanded on that term since 2004. They published a report on the Creative Economy, understood to mean the sum of creativity, culture, economy and technology, “an evolving concept based on the creative advantages generated by economic growth and development, which creates employment, exports, while promoting social inclusion, cultural diversity and human development”.

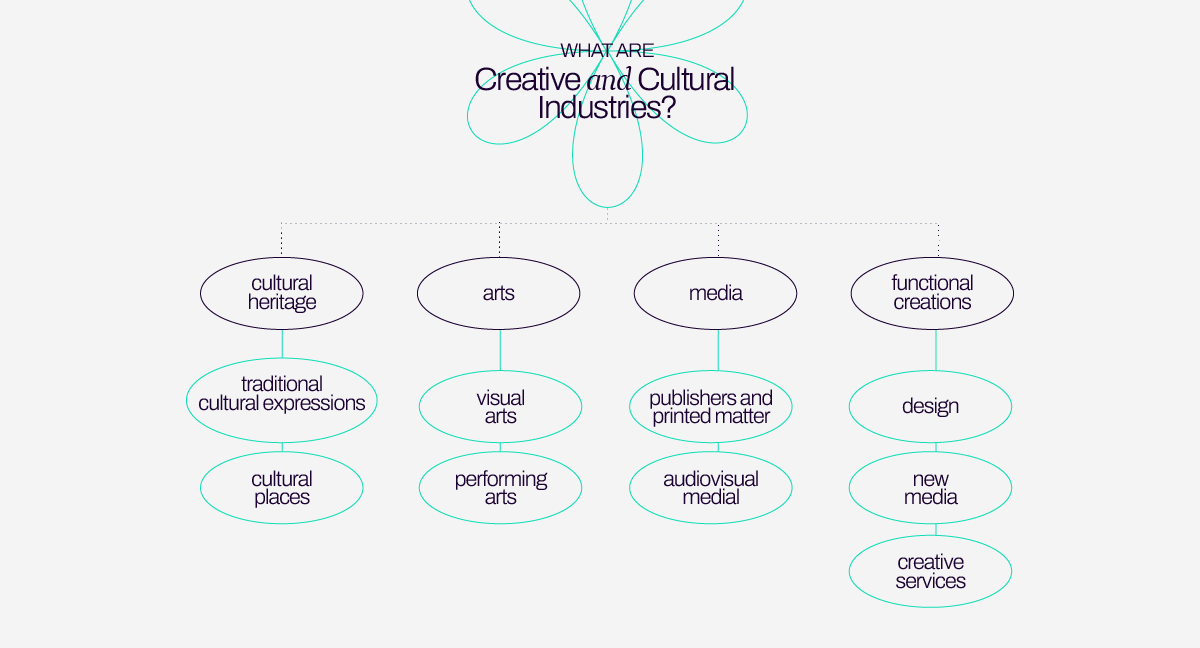
When it comes to the classification of the UNCTAD, they divide the Creative and Cultural Industries as it follows:
Cultural heritage:
Cultural heritage brings with it cultural-historical, anthropological, ethnic, aesthetic, social aspects and influences creativity, it is the origin of a number of heritage goods and services, as well as cultural activities.
- Traditional cultural expressions: crafts, festivals and celebrations
- Cultural places: museums, libraries, exhibitions, etc
Arts:
Works classified in this category are inspired by heritage, values of identity, symbolic meanings and self expression that had a high density of creation that would be eligible for copyright.
- Visual arts: Painting, sculpture, photography and antiques
- Performing arts: live music, theatre, dance, opera, circuses, puppet shows, etc.
Media:
Media is defined as the production of creative content with the aim of communicating with large audiences.
- Publishers and printed matter: books, press and other publications
- Audiovisual media: films, television, radio and other types of dissemination
Functional creations:
This group is oriented towards demand and goods and services with functional purposes.
- Design: interior, fashion, jewellery, graphic design and toys
- New media: computer games, human-computer interfaces, interactive computer installations, virtual reality
- Creative services: architecture, advertising, cultural and recreational services, creative research and development (R&D), digitalization and other related creative services